NUTRITIOUSANDNICE.COM
Regulating the Homeodynamic body
Hormones, Neurotransmitters and cytokines play a significant role in regulating the body. Individual cells release interferons when it is infected by a virus, which stimulates nearby cells in combating further infection, and signals the immune system into mounting an appropriate response. Differing cytokines are released by individual cells which also help the body in mounting an appropriate response by the Immune system. The Endocrine system produces hormones which play a significant role in regulating many processes within the body. The Nervous system uses electrical signalling to produce a response. However the three systems may interact and influence each others functioning. An example of this is the way cortisol release in times of stress will impact upon the immune response. Hormones do not act in isolation and there is a complex relationship between individual hormones and the immune and nervous systems.
Cells of the body have receptor sites which once stimulated will produce a response. There are different mechanisms whereby this response will occur. Lifestyle, diet, and the environment play a significant role in modifying responses. Below is a list of the differing types of regulators, but it is worth keeping in mind that there is an interaction between the differing regulatory systems, and that each one may have a variety of functions.
Types of regulators
Type |
Produced From |
Function |
Prostaglandins |
Arachidonic acid and Essential Fatty Acids |
Cellular regulation: pro and anti-inflammatory |
Nitric Oxide |
Arginine |
Immune, neurological and vascular effects |
Dopamine, Seretonin, Acetylcholine |
Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Choline |
Neurotransmitter |
Cortisol, Aldosterone |
Cholesterol |
Stress Hormone and electrolyte control |
Estrogen, Testosterone, DHEA |
Cholesterol |
Sex Hormones |
Melatonin |
Tryptophan |
Sleep Regulation |
NMDA, Glutamate |
Aspartic and Glutamic acids |
Excitotoxins |
Endorphins |
Polypeptides |
Pain and Immune Regulation |
Insulin, Glucagon, Somatostatin |
Polypeptides |
Blood Sugar control |
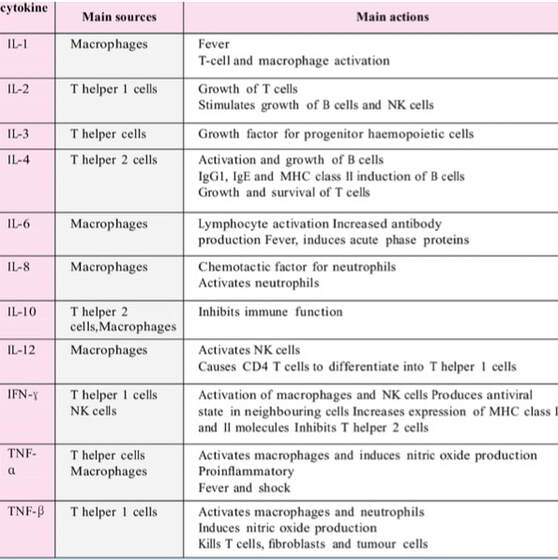
Interleukins, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Interferon |
Protein |
Inflammatory Response |
Leptin |
Protein |
Apetite Control |
Vasopressin, ACTH, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone, Oxytocin |
Polypeptides |
Pituitary Hormones |
Bombesin, Vasoactive intestinal peptide |
Polypeptides |
Gut-Brain transmitters |
C-reactive protein and Sodium amyloid A |
Protein and protein-carbohydrate complex |
Inflammatory markers |
NFkB/IkB |
Protein |
Control of Oxidant response |
ICAM/VCAM |
Protein |
Cellular and Vascular Adhesion |